What is the difference between 201 stainless steel and 304 stainless steel?
 What is the difference between 201 st...
What is the difference between 201 st...Forging means a processing method that causes metal from impact or pressure between the metal, the undervolate iron or forging. It can be divided into free forging and model forging.
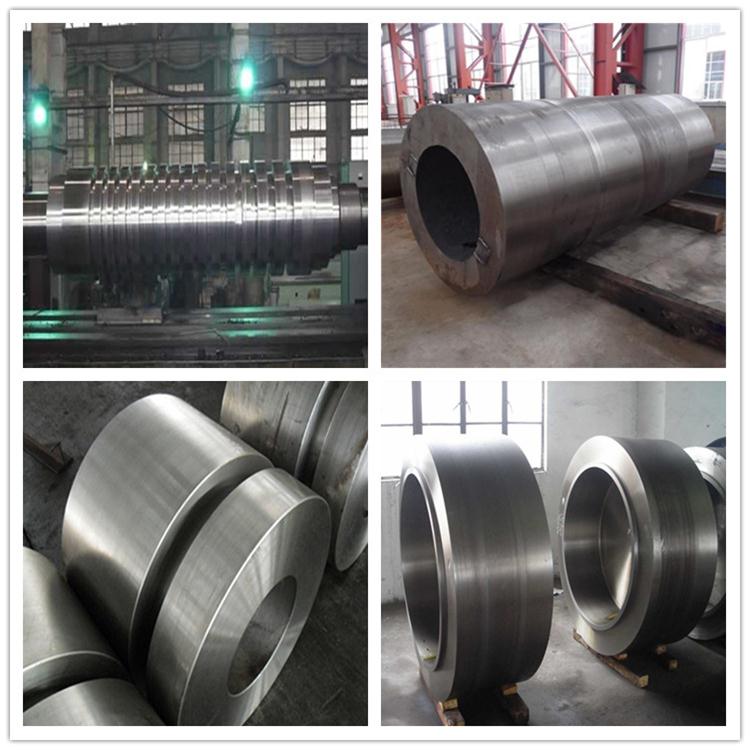

Free forging is a machining method that is freely forged by means of impact or pressure to obtain metals in each direction between the upper and lower anvil, and is not subject to any processing method of obtaining the desired shape and size and a certain mechanical properties, referred to as free forging.

If the shape of the workpiece is the only requirement, the forging is only one of many molded processes. However, in many cases, forging is the only way to achieve the necessary mechanical properties. In order to obtain all the advantages of the forging process, the requirements for its performance must be indicated in the forging process specification. Process specification should include a requirement for material standards and any additional requirements, as well as possible exceptions. In addition, the required minimum tensile properties should also be indicated and the maximum and minimum hardness at a particular location of the part.

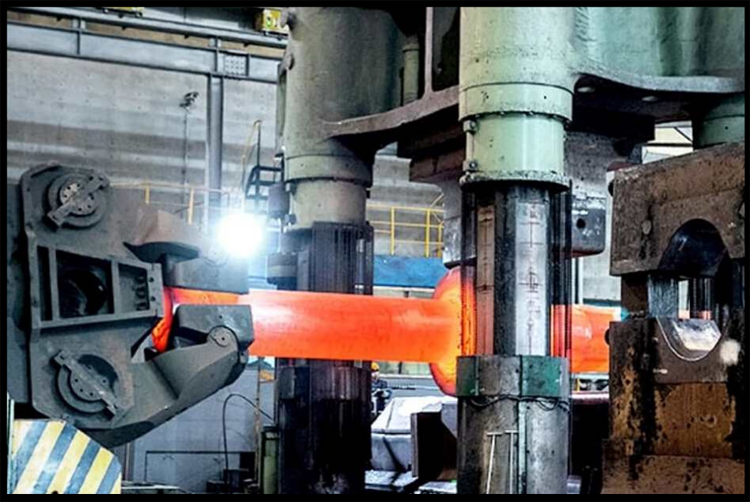
When free forging, the metal is processed on the ground and the undervolar iron is deformed, and the metal can flow freely in the respective directions of the horizontal plane, so it is called free forging.
Free forging equipment and tools are very versatile, and the quality of the forgings is different. However, the shape and size of free forgings mainly rely mainly on the operational techniques of forging to ensure that the technical level of the forging is high, the labor intensity is large, the productivity is low, the precision of the forgings is low, and the processing margin is large, and more complex shape. So mainly used for single-piece, small batch production and repair work. For large forgings, free forging is the only production method.

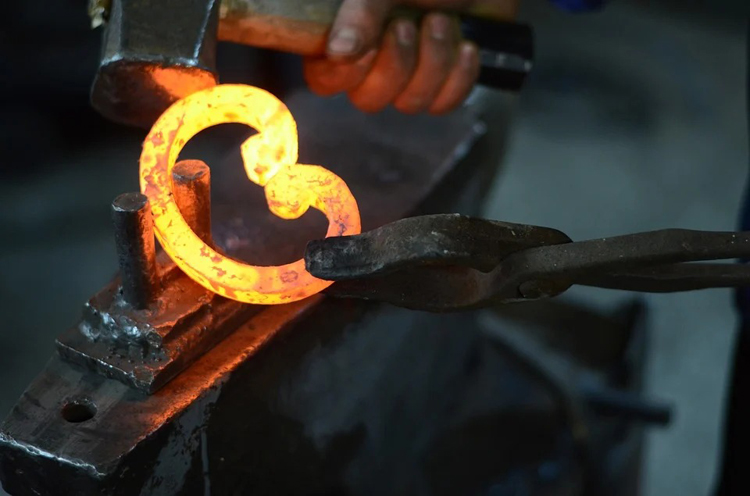
Free forged manual forged and machine forging.
Handmade forging is a tool for making a forgings by utilization using an anvil iron, a large hammer, a hammer, a handmeter, a punch, a chisel, and a hammer. The equipment and tools used by hand-forged, there are few investments, but the labor intensity is large, low productivity, suitable for repair work and auxiliary work for machine forging.
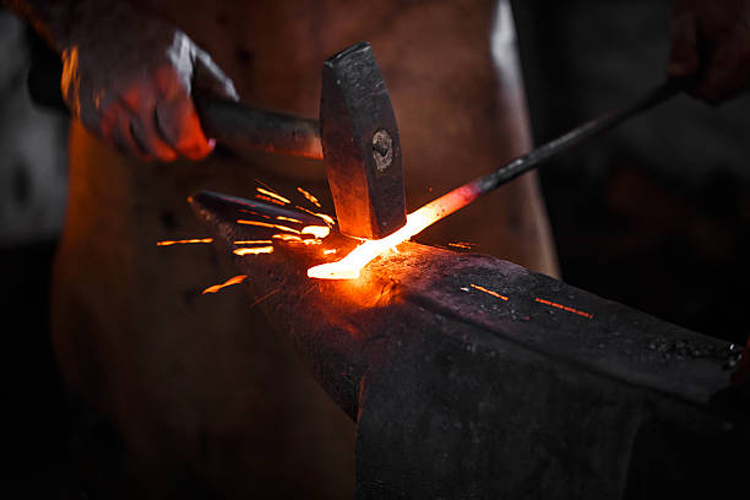

Manual forging is operated by the palm aggressions and hopper. The palm of the palm is holding the clamp, to hold, move, and flip the workpiece; the right hand holds the homach, used for a small amount of wrought and command hammer. Hold the hammer and hold the big hammer and stand on the outside of the anvil.
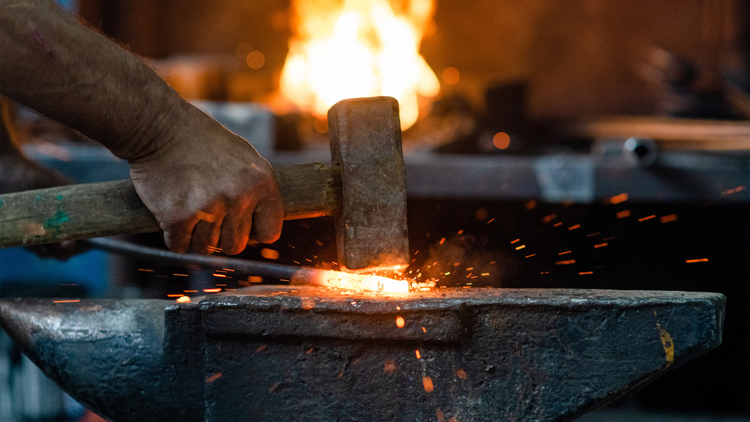

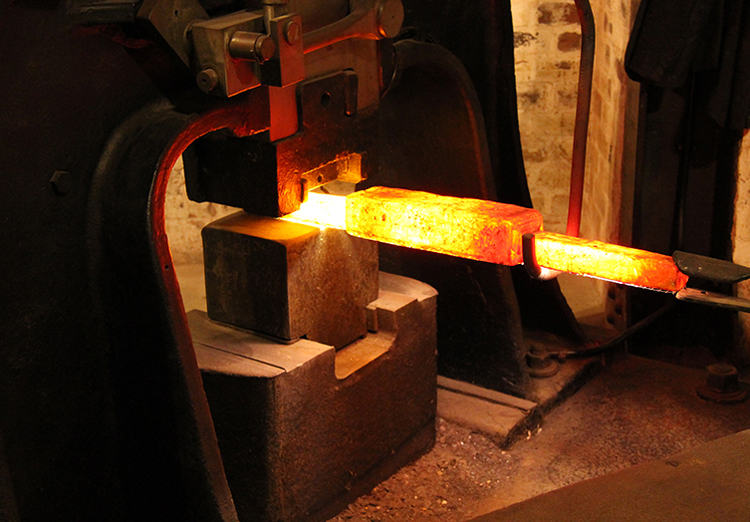
Machine forging is a method of deforming the blank or pressure generated by means of a machine. Its productivity is high, but it is still the basic method of free forging.
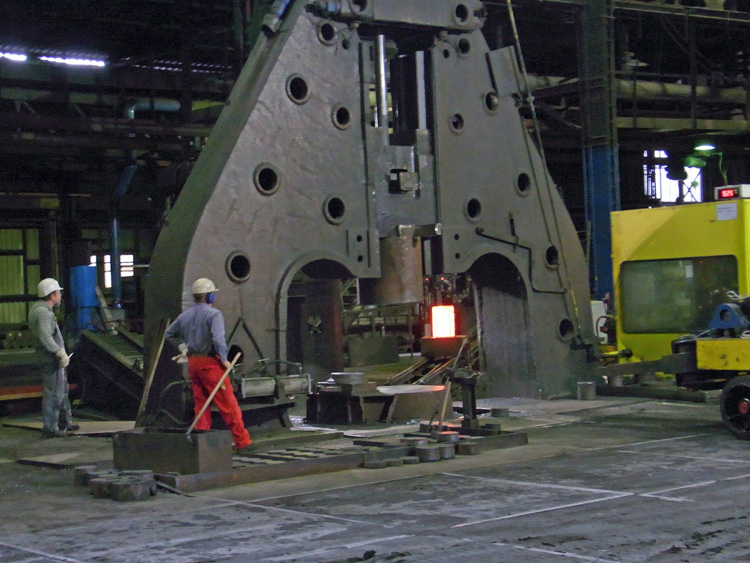

The equipment used by machine forging has air hammers, steam hammers, and water pressure, which are most widely used in air hammers. It has compressed cylinders and work cylinders, and there is a compressed piston in the compressed cylinder, and the motor is moved by the slower mechanism to drive the crank-link mechanism. When the compressed piston rises, the air is pressed into the upper part of the working cylinder, so that the working piston is hit by the hammer head and the anvil iron. When the compression piston is lowered, the air is pressed into the lower portion of the working cylinder, so that the working piston is lifted along with the hammer.

The forming feature of free forging is: the blank is gradually partially deformed between the flank or the tool. Since the tool is partially in contact with the blank, the hysteresis gathers are much smaller than the die forging strips of the same size forgings, so free forging is suitable for forging large forgings.
Advantages of free forging production:
①Free forging can improve the metal and performance of the metal, the quality and mechanical properties of metal free forgings are higher than the casting parts, and their intensity is 50% -70% higher than casting, so it can withstand large impact loads. Under the premise of ensuring the design strength of the parts, reduce the weight of the parts itself, which is important for aerospace and transportation.
②Free forging can save raw materials. The use of a free forging method can produce a piece of shape that is closer to the part.
③Free forging is suitable for single-piece small mass production, and variety changes flexibility.
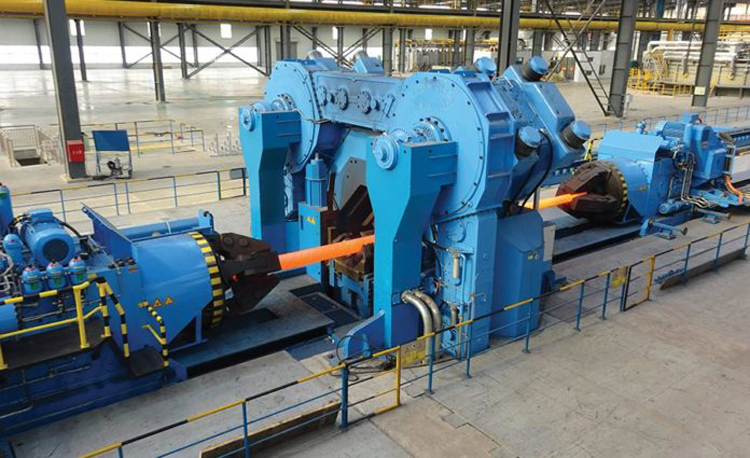

④Direct axis or curved strips and annular parts due to the golden sessions, and their streamline distribution is generally reasonable than the integer for forgings. It is particularly suitable for a simple shape, a small cross-sectional line or a curved shaft element, disk class or an annular member that is flat, and the spindle is flat.
⑤Some special torsion requirements can be satisfied by free forged process processes.
Disadvantages of free forging:
①with low use rate of free forged forgings, larger, and the sharpness of the rinserality of the flow lines and the difference between the extent of the outability of the forgings, during the machining process, metal flow Lines are easily cut.
②The mechanical properties of the aluminum alloy free forgings are relatively low compared to the die forging.
③Forging production methods have low production efficiency, mechanization, and automation in other pressure processing methods.
④The degree of forging is not uniform enough, the homogeneity of the same batch of forgings is poor, and the complex forgings are much longer than the fire, and only the individual parts are only heated without participating in deformation, thus may result The occurrence of uneven or low-altitude is low.
⑤and die forging comparisons, the quality of free forgings is more affected by forging processes and longing operating levels.
 What is the difference between 201 st...
What is the difference between 201 st... Why is 316 stainless steel better tha...
Why is 316 stainless steel better tha... 400 series stainless steel science
40...
400 series stainless steel science
40... How to distinguish the processing tec...
How to distinguish the processing tec... Non-standard design materials of bras...
Non-standard design materials of bras... What type of titanium alloy does Tc4 ...
What type of titanium alloy does Tc4 ...