What is the difference between 201 stainless steel and 304 stainless steel?
 What is the difference between 201 st...
What is the difference between 201 st...
With modern physics, chemical, metallics and heat treatment such as technologies to change the condition and properties of the part surface to optimize the combination of cardiac materials to achieve a predetermined performance requirement, referred to as surface treatment processes.
The role of surface treatment:
Improve surface corrosion resistance and wear resistance, slowing, eliminate changes in the surface of the material and damage;
Gets common materials to have special functions;
Save energy, reduce costs, and improve the environment.
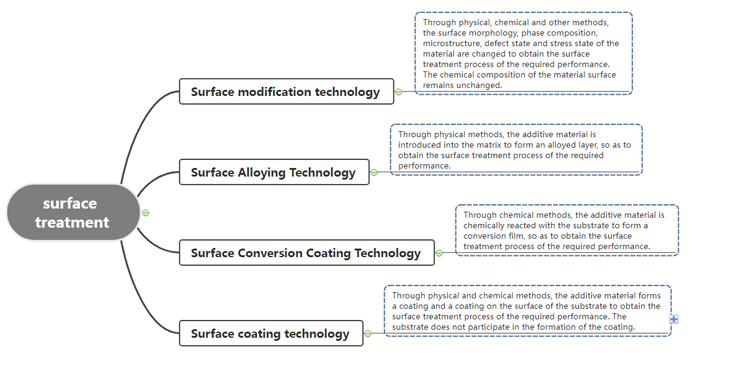
A total of 4 categories: surface modification techniques, surface alloying techniques, surface transformation membrane technology and surface coating techniques.
① surface quenching
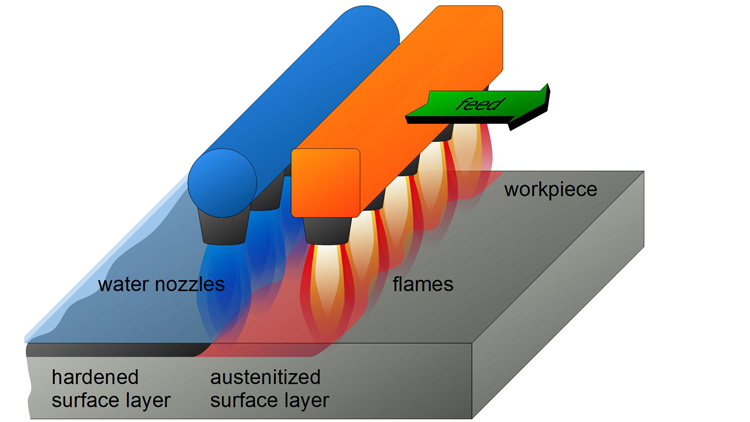
Surface quenching refers to the heat treatment method of the surface of the part after the chemical composition and cardiom tissue does not change the steel, and use rapid heating to strengthen the heat treatment method of the surface of the part.
The main method of surface quenching has flame quenching and induction heating, commonly used thermal source, oxycetylene or oxygen-like flame or the like.
② laser surface strengthening
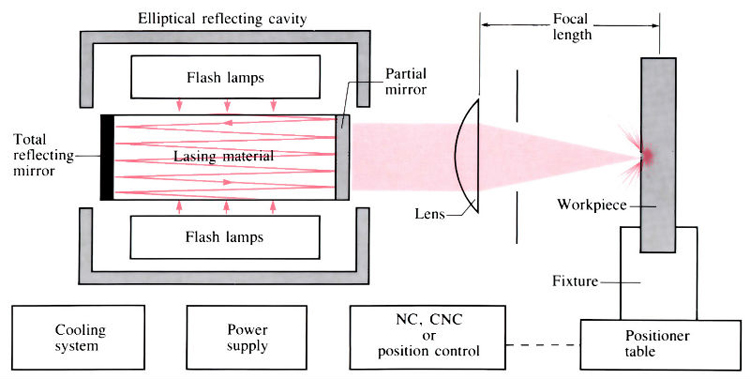
The laser surface strengthening is a focusing laser beam to the surface of the workpiece, which heats the material surface layer very thin to the phase change temperature or the temperature of the melting point in a very short period of time, and continues to be cooled in a very short time. Make the workpiece surface hardenation.
The laser surface strengthening can be divided into laser phase change strengthening treatment, laser surface alloying treatment and laser molten treatment, and the like.
The thermal influence area of the laser surface is small, small deformation, convenient operation, mainly used for local strengthening parts, such as punching mold, crankshaft, cam, camshaft, split axis, precision instrument guide, high speed steel tool, gear and internal combustion engine Cylinder sets, etc.
③shot peening
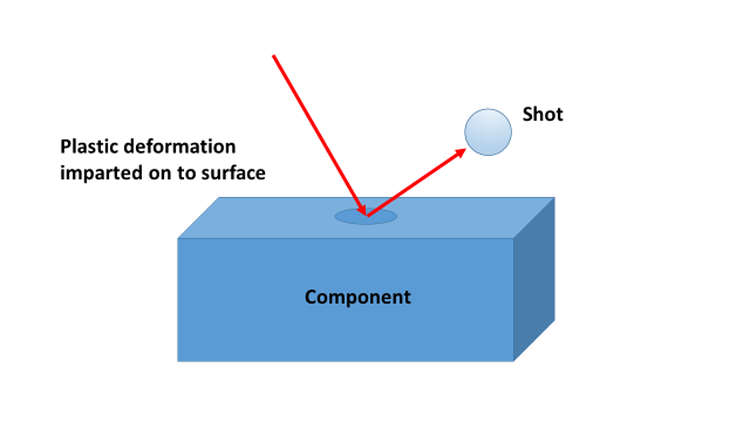
Shot peening is a technique in which a large number of high-speed moving projectiles are sprayed onto the surface of the part, like countless small hammers hammering the metal surface, so that the surface and sub-surface of the part have a certain plastic deformation to achieve strengthening.
effect:
Improve parts mechanical strength and wear resistance, fatigue and corrosion resistance;
Used for surface extinction, remove the oxide layer;
Eliminate the residual stress of casting, forging, and weldments.
④rolling
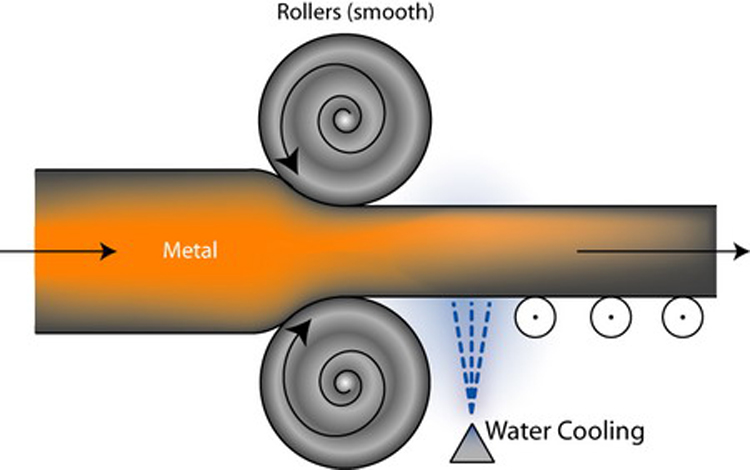
Rolling is to press the surface of the rotating workpiece with a hard roller or a roller at normal temperature, and move along the bus bar to deform the surface of the workpiece, to obtain accurate, smooth and reinforced surface or surface treatment of a particular pattern. Process.
Application: Cylindrical surface, tapered surface, plane and other shaped parts relatively simple parts.
⑤brushed
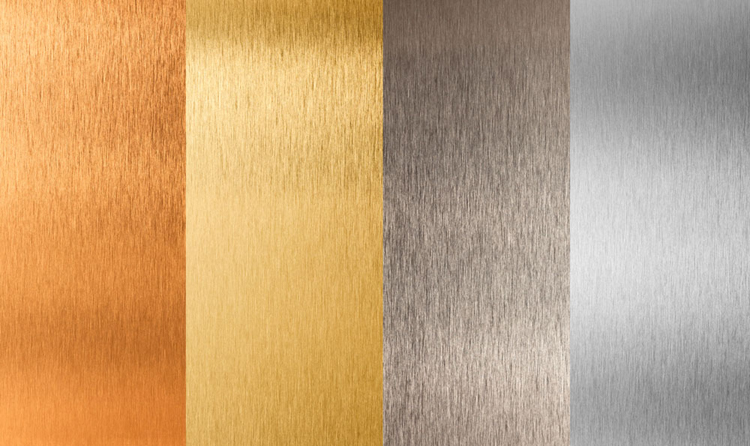

Brushed refers to a surface treatment method of the metal cross-sectional area and the surface treatment method of the metal cross-sectional area and the surface treatment method of the required cross-sectional area and the size of the required cross-sectional area and the surface treatment method of the required cross-sectional area and the size.
The brushes can be made according to the need for decoration, and there is several kinds of straight grain, chaos, corrugation and rotating.
⑥ polishing
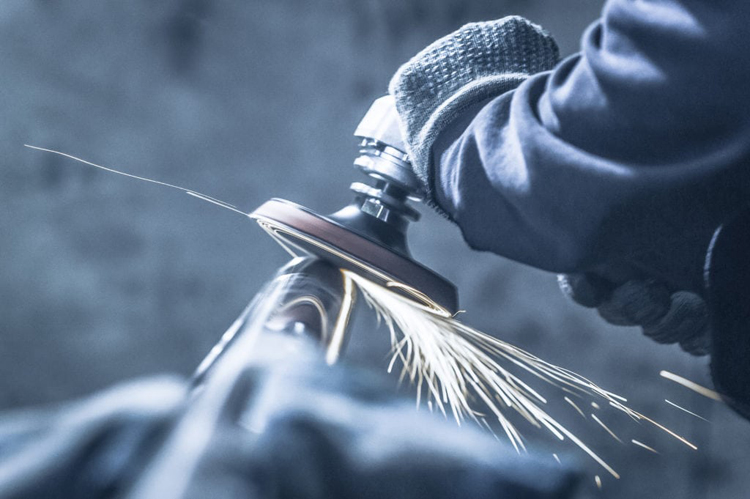

Polishing is a method of modifying the surface surface, generally only obtained smooth surface, can not improve or even maintain the original processing accuracy, different from the pre-machining condition, the RA value after polishing is 1.6 ~ 0.008 μm.
It is generally divided into mechanical polishing and chemical polishing.
Chemical surface heat treatment
Typical processes of surface alloying techniques are chemical surface heat treatment. It is placed in a particular medium to heat the insulation, enabling the active atom in the medium into the workpiece surface to change the surface chemical composition and tissue of the workpiece, thereby changing the heat treatment process of its performance.
Compared to surface quenching, chemical surface heat treatment not only changes the surface tissue of steel, but also changes its chemical composition. Depending on the elements of penetration, chemical heat treatment can be divided into carburizing, nitriding, multi-curated, oozing other elements. The chemical heat treatment process includes three basic processes of decomposition, absorption, diffusion.
The two most important two methods of chemical surface heat treatment are carburizing and nitriding.

①Blackening and phosphating
blackening:
A process in which steel or steel parts are heated to an appropriate temperature in air-water vapor or chemicals to form a blue or black oxide film on the surface. Also become bluish.
Phosphating:
The process in which the workpiece (steel or aluminum, zinc) is immersed in a phosphating solution (some acid phosphate-based solution), and a layer of water-insoluble crystalline phosphate conversion film is deposited on the surface, which is called phosphating .
②Anodizing
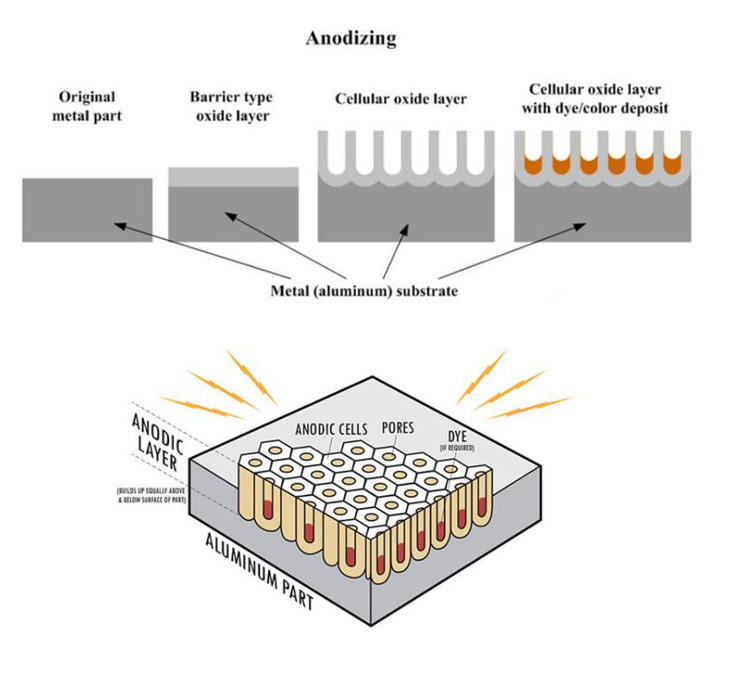
Mainly refers to the anodization of aluminum and aluminum alloys. Anodic oxidation is to immerse aluminum or aluminum alloy parts in an acidic electrolyte, and act as an anode under the action of an external current to form an anti-corrosion oxide film on the surface of the part that is firmly bonded to the substrate. This layer of oxide film has special properties such as protection, decoration, insulation and wear resistance.
Before anodizing, it should undergo pretreatment such as polishing, Degreasing, cleaning, etc., followed by rinsing, coloring, and sealing.
Application: It is often used in the protective treatment of some special parts of automobiles and airplanes, and the decorative treatment of handicrafts and daily hardware products.
①Thermal spraying
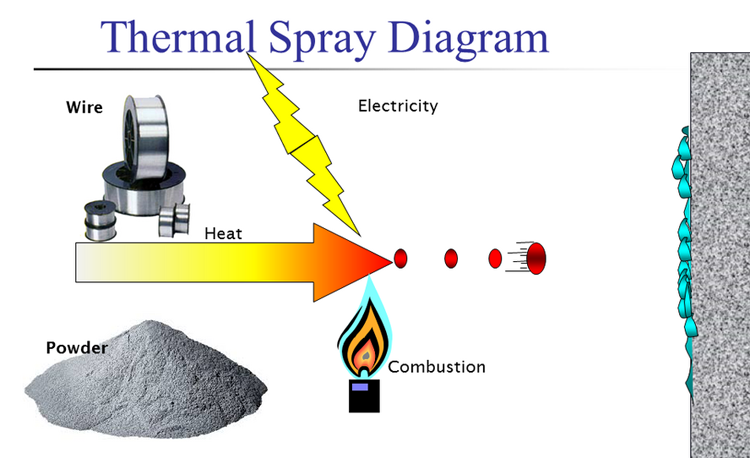
Thermal spraying is to heat and melt metal or non-metallic materials, and continuously spray compressed gas onto the surface of the workpiece to form a coating that is firmly bonded to the substrate, and obtain the required physical and chemical properties from the surface of the workpiece.
The use of thermal spraying technology can improve the wear resistance, corrosion resistance, heat resistance and insulation properties of materials.
Application: almost all fields including aerospace, atomic energy, electronics and other cutting-edge technologies.
②Vacuum plating
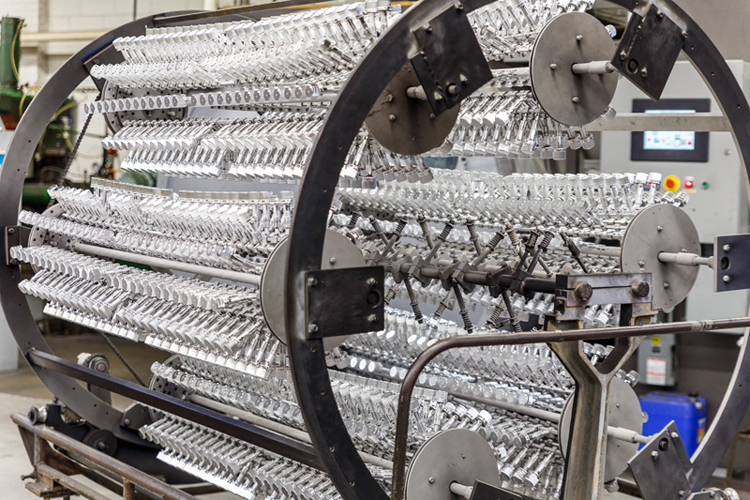

Vacuum plating is a surface treatment process for depositing various metal and non-metal thin films on metal surfaces by distillation or sputtering under vacuum conditions.
A very thin surface coating can be obtained by vacuum plating, which has the advantages of high speed, good adhesion and less pollutants.
According to different processes, vacuum plating can be divided into vacuum evaporation, vacuum sputtering, and vacuum ion plating.
③Electroplating
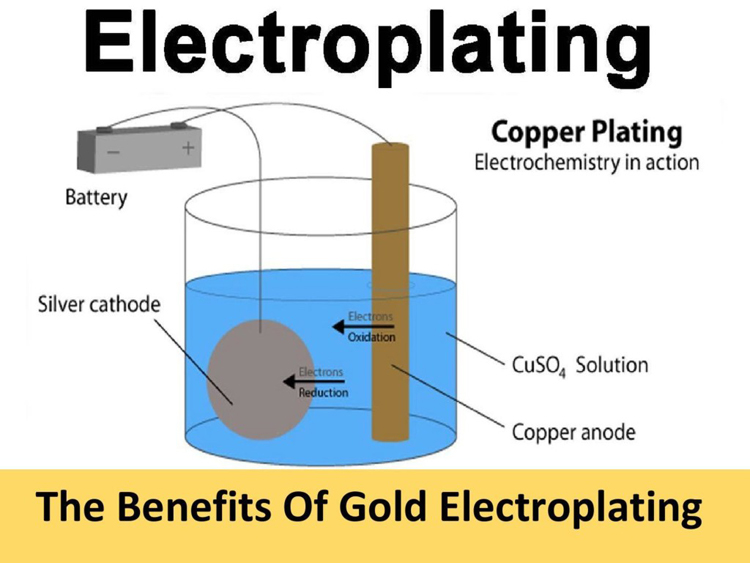
Electroplating is an electrochemical and redox process. Take nickel plating as an example: the metal part is immersed in a solution of metal salt (NiSO4) as the cathode, the metal nickel plate is used as the anode, and after the DC power supply is turned on, the metal nickel layer will be deposited on the part.
Electroplating methods are divided into ordinary electroplating and special electroplating.
④Vapor deposition
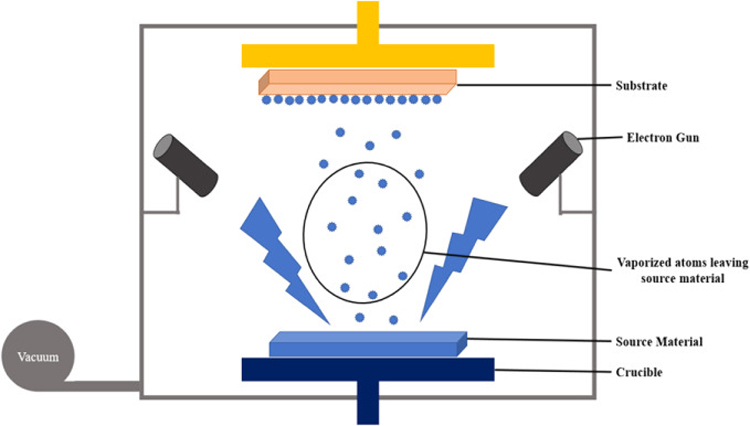
Vapor deposition technology refers to a new type of coating technology that deposits vapor-phase substances containing deposition elements on the surface of materials by physical or chemical methods to form thin films.
According to the principle of deposition process, vapor deposition technology can be divided into two categories: physical vapor deposition (PVD) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
Physical vapor deposition refers to the technology of vaporizing materials into atoms, molecules or ionization into ions by physical methods under vacuum conditions, and depositing a thin film on the surface of materials through a gas phase process.
Physical deposition technology mainly includes three basic methods: vacuum evaporation, sputtering, and ion plating.
Physical vapor deposition has a wide range of applicable substrate materials and film materials; the process is simple, material-saving, and pollution-free; the obtained film has the advantages of strong adhesion to the film base, uniform film thickness, compactness, and fewer pinholes.
It is widely used in the fields of machinery, aerospace, electronics, optics and light industry to prepare thin films such as wear-resistant, corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant, conductive, insulating, optical, magnetic, piezoelectric, lubricating, and superconducting.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Chemical vapor deposition refers to a method in which a mixed gas interacts with the surface of a substrate at a certain temperature to form a metal or compound film on the surface of the substrate.
Because the chemical vapor deposition film has good wear resistance, corrosion resistance, heat resistance and electrical, optical and other special properties, it has been widely used in machinery manufacturing, aerospace, transportation, coal chemical industry and other industrial fields.
 What is the difference between 201 st...
What is the difference between 201 st... Why is 316 stainless steel better tha...
Why is 316 stainless steel better tha... 400 series stainless steel science
40...
400 series stainless steel science
40... How to distinguish the processing tec...
How to distinguish the processing tec... Non-standard design materials of bras...
Non-standard design materials of bras... What type of titanium alloy does Tc4 ...
What type of titanium alloy does Tc4 ...