What is the difference between 201 stainless steel and 304 stainless steel?
 What is the difference between 201 st...
What is the difference between 201 st...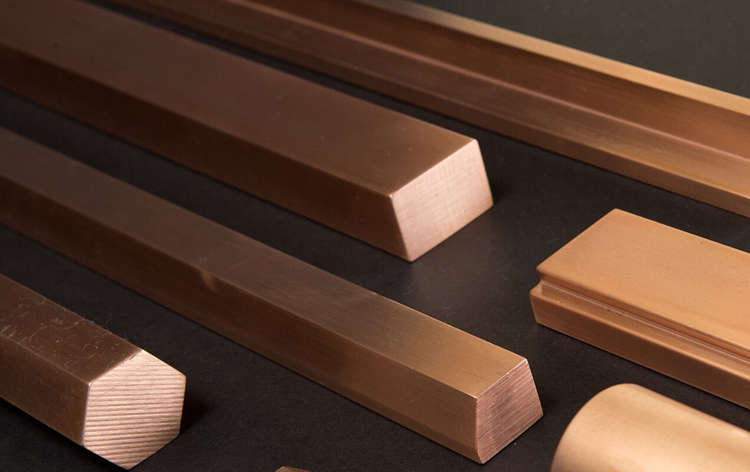
The main purpose of high purification is to increase the conductive and thermal conductivity of the material as much as possible. The copper-containing amount of industrial copper is from 99.90% to 99.95%, and then 99.99% (4N) or even higher, such as a copper 99.9999% (6n) ultrapure copper, the impurity content requirements are also more stringent. The oxygen-containing (O) is reduced from 0.01% to 0.05% to 0.001% to 0.006% until 0.0002% ~ 0.0003%. Maximize impurities on conductivity and thermal conductivity. Typical application instances such as network transmission connection wires, high-purity copper, high-purity and high-fidelity signal transmission and supermixed copper and ultrapine copper, and super pure copper.
Compared with polycrystalline copper, the tensile strength of single crystal copper has decreased by 24.71%, and the elongation increased by 2.39 times. The section shrinkage ratio increased by 4.14 times, and the resistivity is reduced by 31.7%, less than 1.72 × 10-8 Ω · m. The oxygen content is less than 5 × 10-6, and the amount of hydrogen containing is less than 0 ... 5 × 10-6, the density is greater than 8.92 μm.
On the other hand, the copper alloy material develops to the high purification direction is shown in the micro-gold copper alloy to require the high purification of the copper alloy matrix to ensure higher comprehensively.

The purpose of microallization is to sacrifice minimal conductive conductivity exchange for other properties, such as the great improvement of intensity. Such as 0.1% of iron (Fe), magnesium (Mg), TE), silicon (Si)), silver (Ag), titanium (Ti), chromium (Cr) or (Zr), rare earth elements, etc. It can improve its intensity, hardness, softening temperature or easy cutting. Microesed copper is one of the popularities of current copper alloy materials.
The concept of oxygen copper is relatively oxygen-free copper, its copper content is 99.90%, which is equivalent to general pure copper, but its oxygen content is controlled at 0.005% to 0.02%, and the conductivity can be achieved at 100% IACS. . This is because the appropriate amount of oxygen has been used to a certain oxide moiety to a crystal impurity element, and the substrate is purified to some extent.

High-strength high-spirited copper alloy has been favored by the world's materials science and technology workers due to its good comprehensive performance. It has developed the fastest type of copper alloy in recent years. Its microalloyed added elements include: P, Fe, CR, Zr, Ni, Si, Ag, Sn, Al, etc., which have a representative alloy system mainly include Cu-P, Cu-Fe-P, Cu- Ni-Si, Cu-Cr, Cu-Cr-Zr system, Cu-Ag, Cu-Ag-Cr, Cu-Ag-Zr system, Cu-SN system, etc., and alloying systems with various rare earths. The sum of other components in the alloy may be from 0.01% to 0.1%, and the highest is generally not more than 3%. Its common feature is that the material has high high-spirited performance.

In order to further improve the strength, corrosion resistance, wear resistance and other properties of the copper and its alloys, or to meet certain special application requirements, add more than five yuan, six yuan, etc. Components, realize high-elasticity, high wear resistance, high corrosion resistance, easy cutting, etc., multi-component (four or more components) alloying into another hot topic developed by copper alloy, new The complex alloy is endless. Typical alloys have multi-manganese brass, silicon-manganese brass, boron copper, lead-free copper alloy, and the like. Its common feature is high-strength high toughness, and the tensile strength is generally up to 600 to 700 MPa. Application of these materials to make automotive synchronizer tooth ring, high-pressure pump friction pair of copper wedges, and its life is more than one to several times higher than ordinary brass or bronze.

In recent years, with the improvement of people's environmental awareness, environmental protection has become the theme of the development of world civilization. People pay more attention to harmful elements such as lead, beryllium, cadmium, and arsenic. The development of environmentally friendly copper alloy materials such as lead-free black-free brass, non-arsenic-resistant copper alloy, etc. One of the development directions.

There are two main methods of copper alloy materials: one is to introduce alloying elements to strengthen the copper matrix formation alloy; the second is to introduce a second strengthening phase to form a composite material. If the dispersion of reinforced oxygen-free copper is a typical artificial composite material, there are commonly used dispersion sites with Al2O3, ZrO2, Y2O3, Tho2, etc. The artificial composite method refers to the granules of the addition of the second phase to the copper, and the whiskers or fibers are enhanced to the copper base. By introducing uniformly distributed, small, fine, well-thermally stable oxide particles to be strengthened by introducing the copper group. Materials made by copper. The second phase of the second phase is generally below 1% or even lower to 0.01%, but the enhancement of the material is very obvious, especially the high temperature strength of the material is greatly improved. Such as Cu-2.5% TiB2 (volume fraction), the conductivity is 76% LACS, the tensile strength is 675 MPa; Cu-0.5% Al2O3 (mass fraction) series alloy, the temperature of the material can reach 500 ~ 800MPa, the conductivity is up to 85% LACS above, the strength of the material after the hydrogen in 900 ° C is still reached from 200 to 400 MPa.

Another type of developer is the in situ composite, and the in situ composite is a class of composite materials that generate a reinforcing body between the copper matrix, between the altimeters or the exothermic reaction. The reinforcing bodies in such composites do not have interface pollution, with a good interface compatibility with the substrate, which has a large increase in strength compared to the traditional artificial plus enhancement composites, while maintaining better toughness and good High temperature performance.
 What is the difference between 201 st...
What is the difference between 201 st... Why is 316 stainless steel better tha...
Why is 316 stainless steel better tha... 400 series stainless steel science
40...
400 series stainless steel science
40... How to distinguish the processing tec...
How to distinguish the processing tec... Non-standard design materials of bras...
Non-standard design materials of bras... What type of titanium alloy does Tc4 ...
What type of titanium alloy does Tc4 ...