What is the difference between 201 stainless steel and 304 stainless steel?
 What is the difference between 201 st...
What is the difference between 201 st...Castings made of aluminum alloys are widely used in various industries. Especially since the lightweight of automobiles, aluminum alloys are favored by the automobile industry due to their advantages of light weight and corrosion resistance.
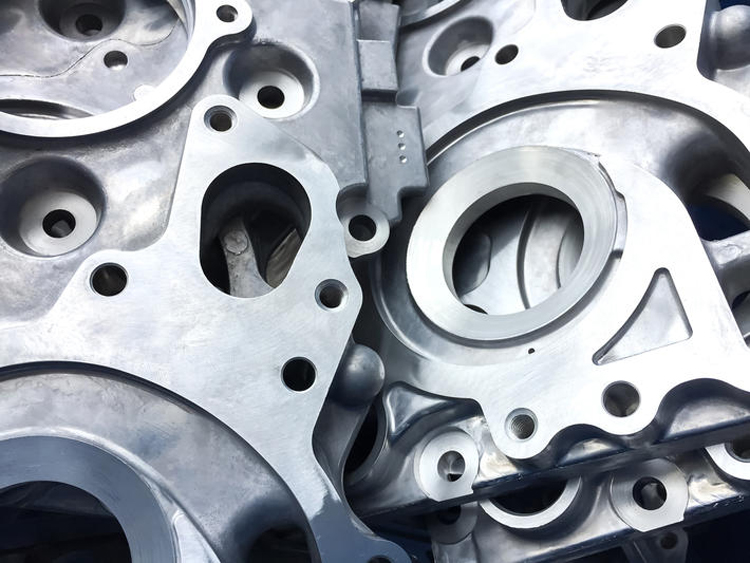
Aluminum alloy has good surface gloss and good corrosion resistance in the atmosphere and fresh water. Pure aluminum has good corrosion resistance in oxidizing acid media such as nitric acid and acetic acid, so aluminum castings are widely used in the automotive industry.

The density of cast aluminum alloy is lower than that of cast iron and cast steel, and the strength is relatively high. Therefore, the use of aluminum alloy castings under the same load conditions can reduce the weight of the structure. The cylinder head in automobiles is a special aluminum casting product. The purpose of using aluminum castings is that it can withstand large thermal shocks, and the characteristics of aluminum castings are relatively good thermal conductivity. For the cylinder head, it can improve its performance. Thermal efficiency to avoid overheating of components.
How are automotive die castings more valuable:
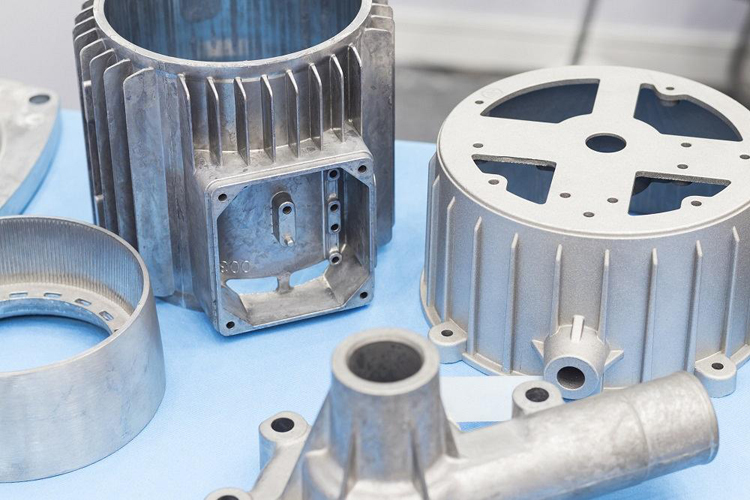
The casting process should be strictly controlled during the use of automobile die castings. Within the allowable range of the process, the casting temperature and injection speed should be reduced as much as possible, and the mold preheating temperature should be increased. Increasing the preheating temperature from 100-130°C to 180-200°C can greatly improve the service life of aluminum alloy die castings.
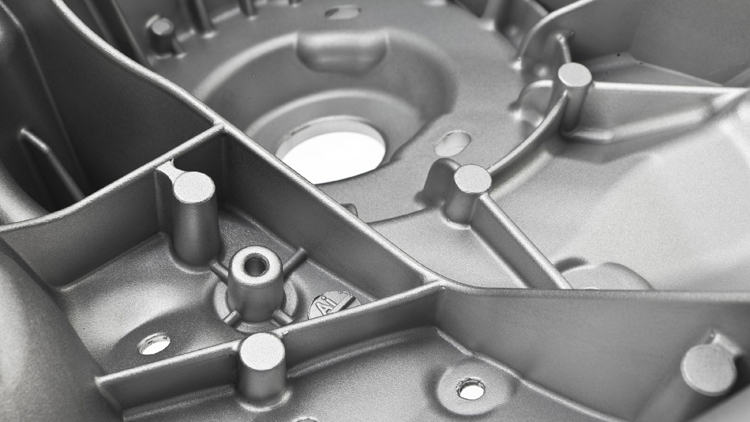
Weld repair is a common method in mold repair. Before welding, direct the steel mold of the welding die and remove surface defects by machining or grinding. The welding surface must be clean and dry. The electrode used should be the same as the die steel and must be clean and dry. The mold is preheated with a welding rod (H13 is 450 ℃), and after the surface temperature is consistent with the core temperature, the mold is repaired by welding under protective gas. During soldering, reheating occurs when the temperature drops below 260°C.
After welding, when the mold is cooled to contact, reheat to 475°C for 25mm/h. Finally, cool completely in still air, then trim and finish the cavity. After welding, the mold is heated and tempered, which is an important part of welding repair, that is, eliminating welding stress and tempering the thin layer under the weld layer that was quenched during welding.
 What is the difference between 201 st...
What is the difference between 201 st... Why is 316 stainless steel better tha...
Why is 316 stainless steel better tha... 400 series stainless steel science
40...
400 series stainless steel science
40... How to distinguish the processing tec...
How to distinguish the processing tec... Non-standard design materials of bras...
Non-standard design materials of bras... What type of titanium alloy does Tc4 ...
What type of titanium alloy does Tc4 ...