What is the difference between 201 stainless steel and 304 stainless steel?
 What is the difference between 201 st...
What is the difference between 201 st...Die casting includes high pressure die casting (HPDC); low pressure die casting (LPDC); gravity squeeze casting (GDC); EMP specializes in high pressure die casting;

Die casting machines are generally divided into cold chamber die casting machines and hot chamber die casting machines.
Cold chamber die casting machines are divided into horizontal die casting machines and vertical die casting machines according to their cavity structure and layout.
The following is the process flow chart of high pressure die casting: raw material melting, die casting, degassing, deburring, trimming, shot peening, CNC machining, leak test, cleaning, full inspection, packaging and delivery.

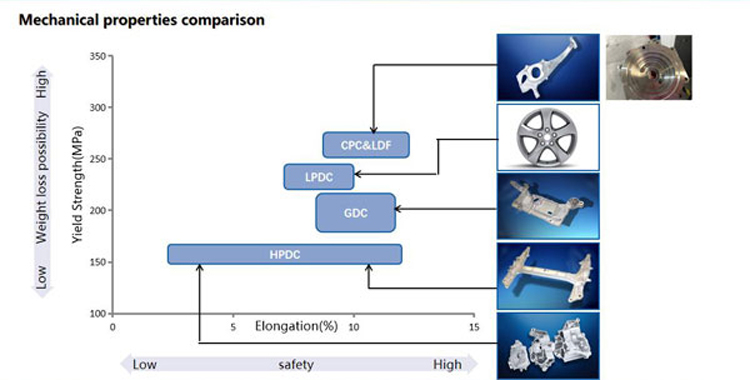
Casting Process | Process | Tooling Cost | Tooling Life | Porosity | Heat treatment | Allowance | Surface cleaning | Part | Productivity |
HPDC | Complex | High | Short | Poor | No | Small | High | Thin-wall | High |
Squeeze Casting | Complex | High | Short | Good | Yes | Small | High | thick-wall | High |
GDC | Simple | Low | Long | Good | Yes | Large | Low | thick-wall | Low |
CPC | Simple | Low | Long | Good | Yes | Large | High | thick-wall | Middle |
LPDC | Simple | Low | Long | Good | Yes | Large | Middle | thick-wall | Middle |
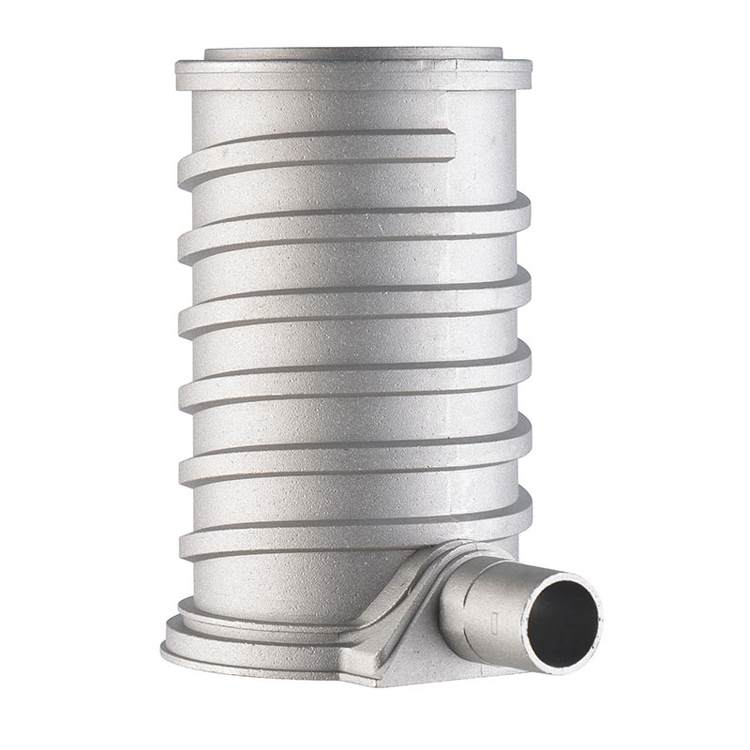

Aluminum alloy die castings have the advantages of high production efficiency, low processing costs, easy mechanical automation of the production process, high dimensional accuracy of castings, good surface quality, and good overall mechanical properties.
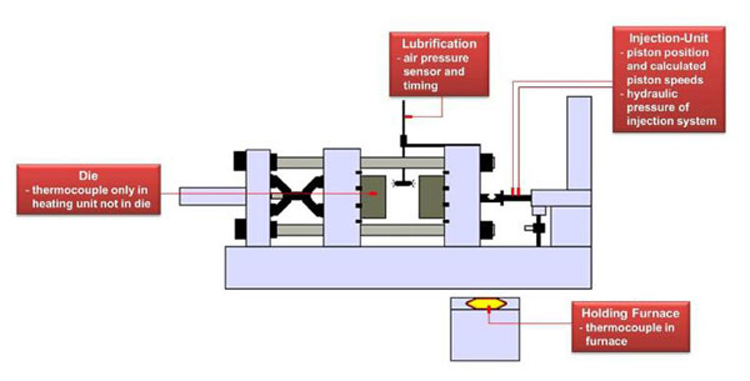
Aluminum alloy die castings must be formed by molds and combined with die casting machines and aluminum alloys to be comprehensively utilized. The principle of the die casting process is that molten metal is injected into the cavity of a precision metal mold at high speed under high pressure, and then cooled and solidified into a casting under pressure. Cold chamber die casting and hot chamber die casting are two basic methods of die casting process. In cold chamber die casting, liquid metal is injected into the cold chamber by a manual or automatic casting device, and then the injection punch moves forward and presses the liquid metal into the cold chamber. In the process of hot chamber die casting, the pressure chamber is perpendicular to the crucible, and the molten metal automatically flows into the pressure chamber through the feed port on the pressure chamber. The injection punch moves down, pushing the molten metal into the cavity through the gooseneck. After the molten metal solidifies, the die-casting mold is opened, the casting is taken out, and the entire die-casting molding process is completed.
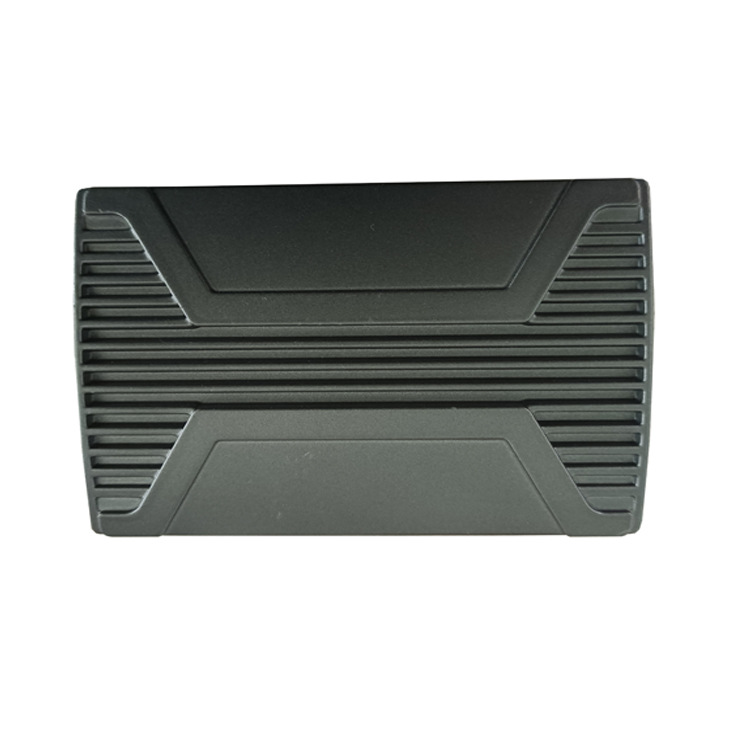

In the process of manufacturing aluminum alloy die castings, the surface processing quality of the cavity can be effectively improved. There should be no obvious deep processing marks on the surface of the mold cavity to prevent the mold from cracking due to stress concentration during the working process. After the mold is completed, the cavity surface should be effectively polished and ground to keep the cavity surface roughness below 0.8μm.
Die-casting mold is an important process equipment in die-casting production. The molten metal cools and solidifies in a die casting mold to form a die casting. The shape, size, quality and smoothness of die-casting production are closely related to the die-casting mold, so it's very important to design a correct and reasonable die-casting mold.
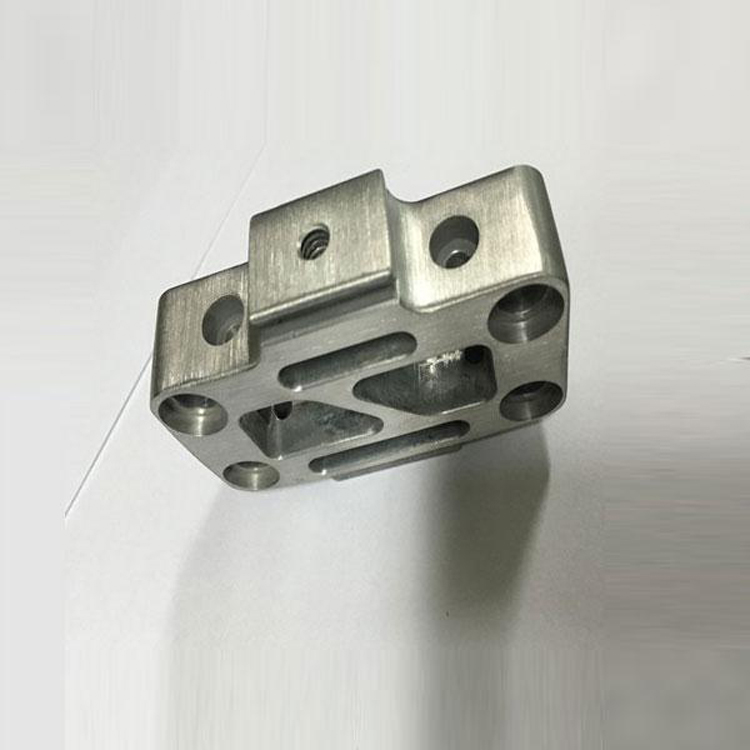

Die casting mold design should pay attention to the following points:
(1) Try to adopt an advanced and simple structure to ensure stable and reliable operation and facilitate daily maintenance and repair.
(2) Considering the modifiability of the gating system, necessary modifications can be made during the commissioning process.
(3) Reasonable selection of tolerances, scales and machining allowances to ensure reliable mold fit and required die casting accuracy.
(4) Select the appropriate mold material and reliable heat treatment process to ensure the service life of the die-casting mold.
(5) It should have sufficient rigidity and strength, and be able to withstand the clamping pressure and expansion force during die casting production without deformation.
(6) Use standardized die casting mold parts as much as possible to improve economy and interchangeability.
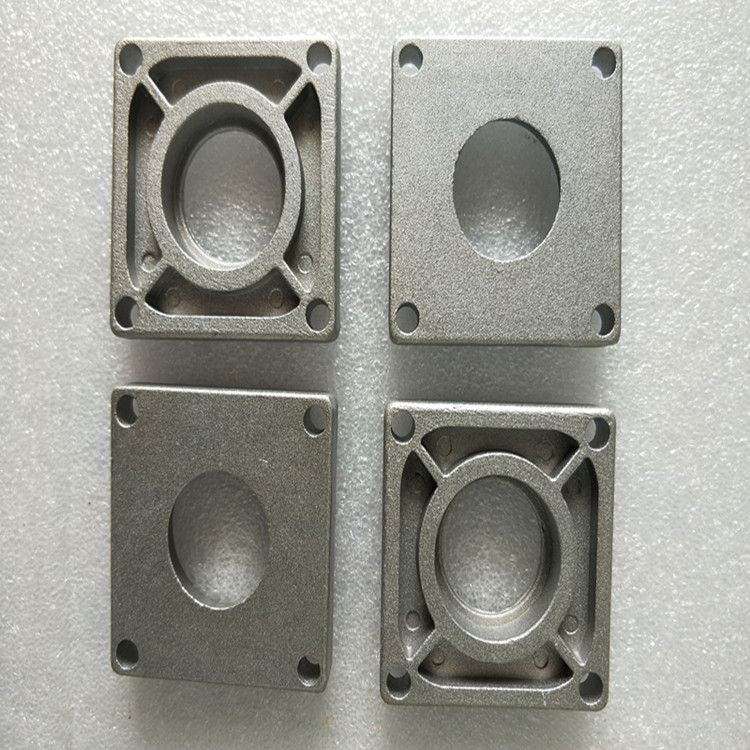

Die castings are widely used in all walks of life, and the market demand is huge. However, in the production process, aluminum alloy die castings are prone to scratches, and in severe cases, scratches may occur.
Reasons for drag marks on aluminum alloy die castings:
(1) The mold temperature is higher than 220 degrees, and the casting is easy to scratch or stick to aluminum.
(2) The iron content of the aluminum alloy is less than 0.6%, and the aluminum material has an affinity with the mold, which causes the casting to be scratched or stuck.
(3) The ejection of the casting is not parallel, causing the casting to be pulled or deformed.
(4) The surface of the mold core is rough, causing the surface of the casting to be deformed or rough.
(5) The draft angle of the core and wall of the casting is too small, which causes the casting to be scratched during parting.
(6) Insufficient spraying of release agent will also cause drag marks.
 What is the difference between 201 st...
What is the difference between 201 st... Why is 316 stainless steel better tha...
Why is 316 stainless steel better tha... 400 series stainless steel science
40...
400 series stainless steel science
40... How to distinguish the processing tec...
How to distinguish the processing tec... Non-standard design materials of bras...
Non-standard design materials of bras... What type of titanium alloy does Tc4 ...
What type of titanium alloy does Tc4 ...