What is the difference between 201 stainless steel and 304 stainless steel?
 What is the difference between 201 st...
What is the difference between 201 st...Etching is a technique that uses chemical strong acid etching, mechanical polishing or electrochemical electrolysis to treat the surface of objects. In addition to enhancing the aesthetics, it also increases the added value of the item. From traditional metal processing to high-tech semiconductor manufacturing, etching technology is within the scope of application.

Metal etching is a technique for removing metallic materials through chemical reaction or physical shock. Metal etching techniques can be divided into wet etching and dry etching. Metal etching consists of a series of chemical processes. Different etchants have different corrosion properties and strengths on different metal materials.
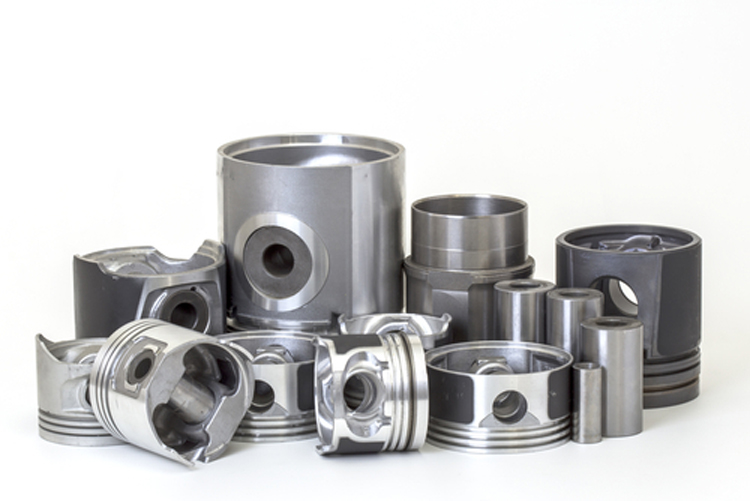

Metal etching, also known as photochemical etching, refers to the removal of the protective film in the metal etching area after exposure, plate making, development and contact with chemical solutions during the metal etching process, so as to dissolve corrosion, form bumps, or hollow out. It was first used to manufacture printed embossed plates such as copper plates and zinc plates. It is widely used to reduce the weight of instrument panels or to process thin workpieces such as nameplates. Through the continuous improvement of technology and process equipment, etching technology has been applied to aerospace, mechanical, chemical and semiconductor manufacturing processes for the processing of precision metal etching products for electronic thin parts.
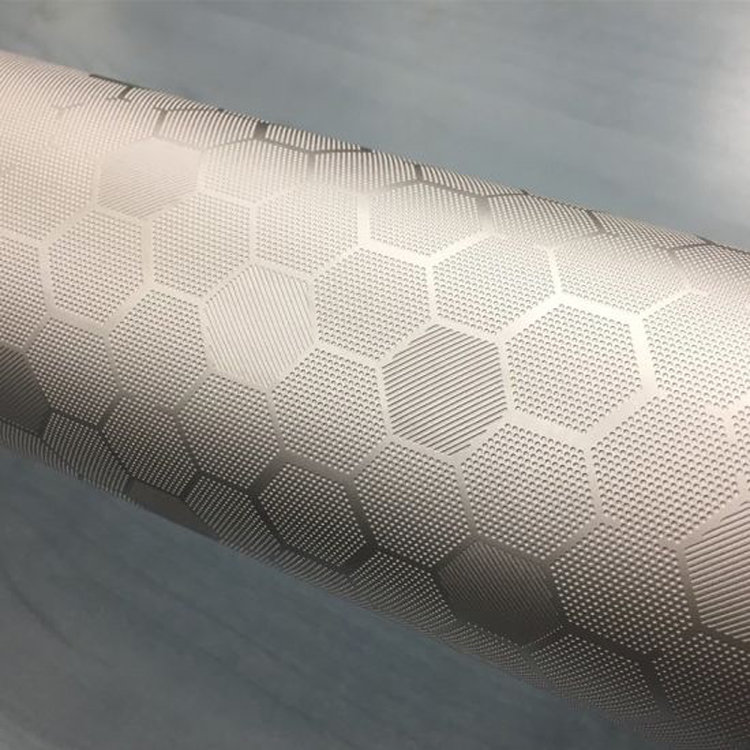
Wet etching is to immerse the wafer in a suitable chemical solution or spray the chemical solution onto the wafer for quenching, and remove the atoms on the surface of the film through the chemical reaction between the solution and the object to be etched, so as to achieve the purpose of etching. During etching, the reactants in the solution first diffuse through the stagnant boundary layer and then reach the wafer surface to produce various products through chemical reactions. The products of the etching chemical reaction are liquid or gas phase products, which then diffuse through the boundary layer and dissolve in the main solution. Wet etching will not only etch in the vertical direction, but also produce the effect of horizontal etching.
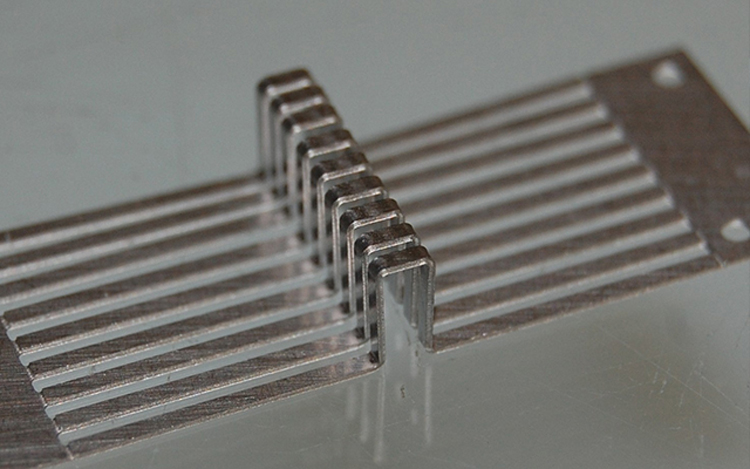
Dry etching is usually one of plasma etching or chemical etching. Due to the different etching effects, the physical atoms of ions in the plasma, the chemical reactions of reactive radicals and device (wafer) surface atoms, or a combination of the two, including the following:
1) Physical etching: sputter etching, ion beam etching
2) Chemical etching: plasma etching
3) Physicochemical compound etching: reactive ion etching (RIE)
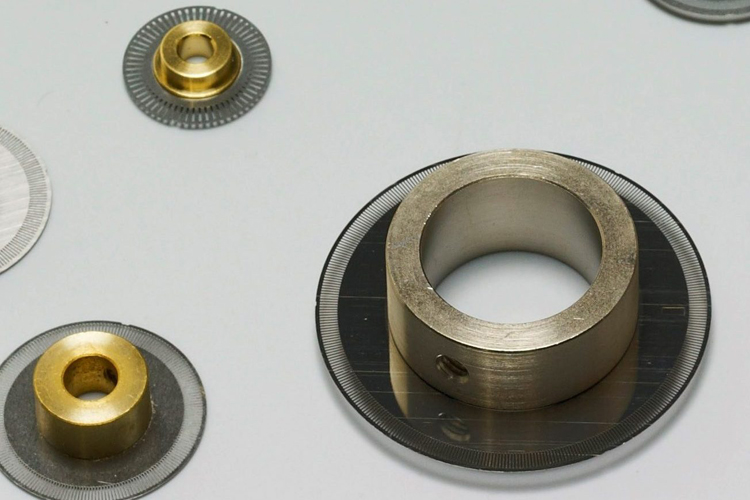

Dry etching is a type of anisotropic etching, with good directionality but poorer selectivity than wet etching. In plasma etching, plasma is a partially dissociated gas, and gas molecules are dissociated into electrons, ions and other substances with high chemical activity. The biggest advantage of dry etching is "anisotropic etching". However, the selectivity of dry etching is lower than that of wet etching. This is because the etching mechanism of dry etching is physical interaction; therefore, the impact of ions can remove not only the etching film but also the photoresist mask.
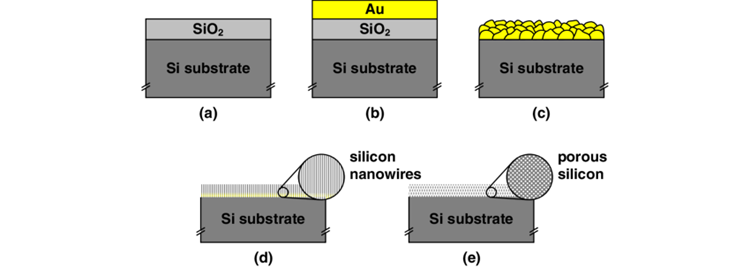
Depending on the type of metal, the etching process will be different, but the general etching process is as follows: metal etching plate → cleaning and degreasing → water washing → drying → coating or screen printing ink → drying → exposure drawing → development → washing and drying → etching → stripping Film→drying→inspection→finished product packaging.
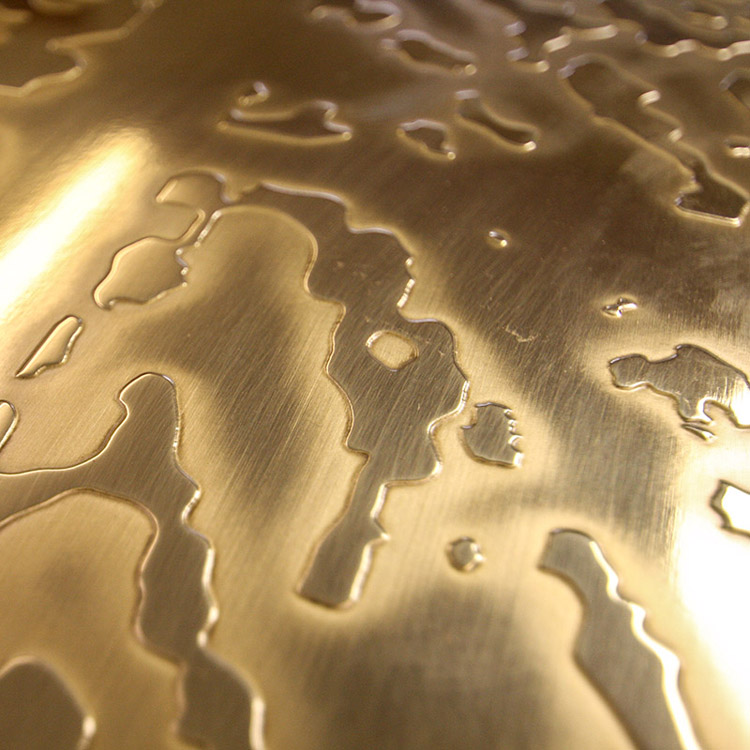

The process before etching stainless steel or other metals is cleaning treatment, which is mainly used to remove dirt, dust, oil stains, etc. on the surface of the material. The cleaning process is the key to ensure that the subsequent film or screen printing ink has good adhesion to the metal surface. Therefore, the oil and oxide film on the metal etched surface must be completely removed. Degreasing should be determined according to the oil contamination of the workpiece. It is best to degrease the screen printing ink before electrodegreasing to ensure the degreasing effect. In addition to the oxide film, the best etching solution should be selected according to the metal type and film thickness to ensure surface cleanliness. Must be dry before screen printing. If there is moisture.
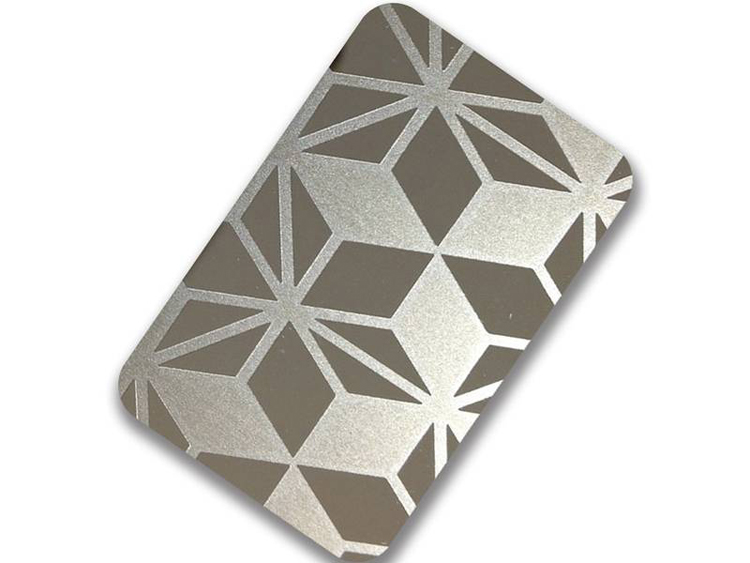

Depending on the actual product material, thickness and exact width of the graphic, determine whether to use dry film or wet film screen printing. For products with different thicknesses, factors such as the etching processing time required for the product pattern should be considered when applying the photosensitive layer. It can make thicker or thinner photoresist layers with good coverage and high definition metal etching patterns.
After the film or roll screen printing ink is completed, the photoresist layer needs to be thoroughly dried in preparation for the exposure process. At the same time, ensure that the surface is clean and free of sticking, impurities, etc.
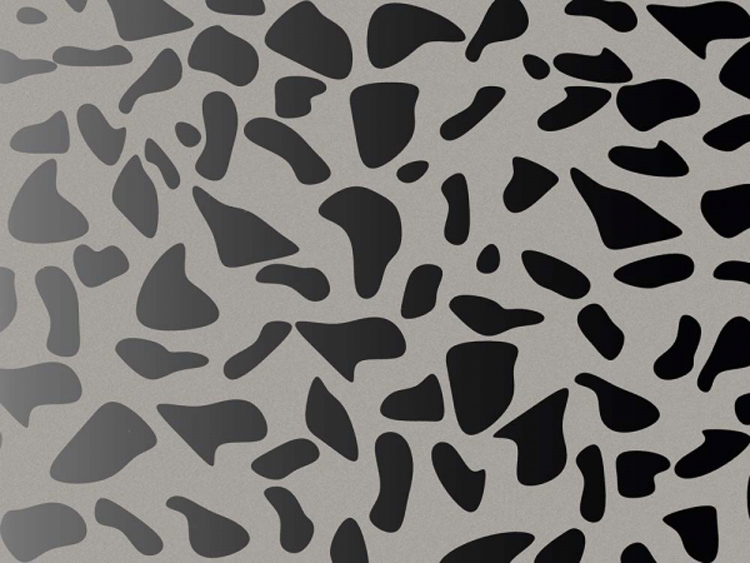

This process is an important process for metal etching, and the exposure energy will be considered according to the thickness and precision of the product material. This is also the embodiment of the technical capabilities of etching enterprises. The exposure process determines whether etching can ensure better dimensional control accuracy and other requirements.
After the photosensitive adhesive layer on the surface of the metal etching plate is exposed, the patterned adhesive layer is cured after exposure. Then, the unwanted parts of the pattern, that is, the parts that need to be etched, are exposed. The development process also determines whether the final size of the product can meet the requirements. This process will completely remove the unnecessary photoresist layer on the product.
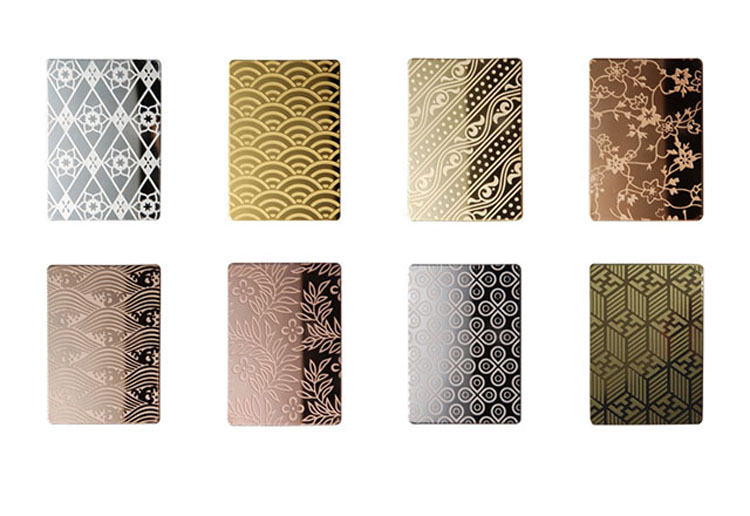

After the product prefabrication process is completed, the chemical solution will be etched. This process determines whether the final product is qualified or not. This process involves the concentration, temperature, pressure, speed and other parameters of the etching solution. The quality of the product needs to be determined by these parameters.
The surface of the etched product is also covered with a layer of photosensitive adhesive, and the photosensitive adhesive layer on the surface of the etched product needs to be removed. Due to the acidity of the photoresist layer, acid-base neutralization is often used for expansion. After overflow cleaning and ultrasonic cleaning, remove the photosensitive adhesive layer on the surface to prevent the photosensitive adhesive from remaining.

After taking the film, the next step is to test, pack, and finally confirm whether the product meets the specifications.
 What is the difference between 201 st...
What is the difference between 201 st... Why is 316 stainless steel better tha...
Why is 316 stainless steel better tha... 400 series stainless steel science
40...
400 series stainless steel science
40... How to distinguish the processing tec...
How to distinguish the processing tec... Non-standard design materials of bras...
Non-standard design materials of bras... What type of titanium alloy does Tc4 ...
What type of titanium alloy does Tc4 ...